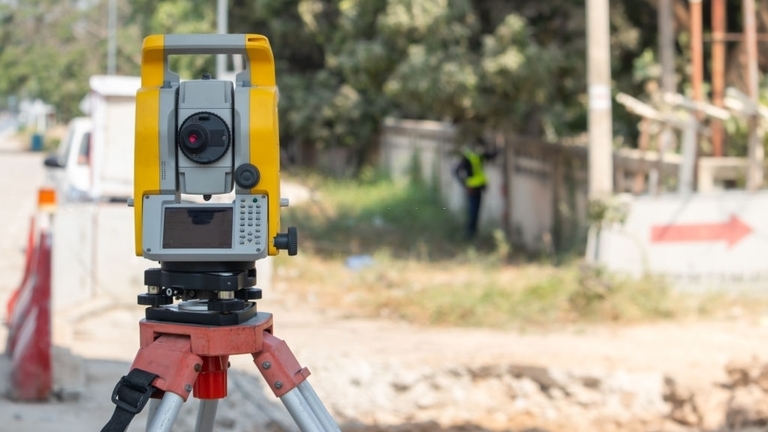
Primarily used to measure vertical and horizontal angles, theodolites are essential to a surveyor’s arsenal. These devices allow surveyors to determine the position of objects at a given site. Today, traditional and digital theodolites are not only used when conducting topographic surveys. Their range of applications also includes meteorology, or the study of the atmosphere and its phenomena.
Electrical meteorological theodolites (e.g. pilot balloon theodolite), in particular, are utilized by weather and climate experts to help them predict meteorological phenomena.
How Theodolites Work
The earliest use of theodolites dates as far back as the 16th century.
Generally, it is composed of a telescope fixed within a vertical and a horizontal axis. The telescope and the mechanisms are housed on a base, which can further be rotated through a leveling system on a tripod.
Compared with other leveling devices, theodolites provide great precision at first reading (meaning, repeat readings are not necessary). Thanks to their internal magnifying optical system, their measurements are not affected by external factors such as weather elements and ground slope.
Additionally, the use of digital theodolites help surveyors obtain more accurate data. Digital readings are also easier and more efficient to work with.
How Theodolites Help Meteorologists
There are different types of theodolites. As stated, these surveying instruments can be used for meteorological purposes.
In the field of meteorology, specially manufactured theodolites are utilized to track ceiling or pilot balloons. These special weather balloons are used to determine the height of the base of clouds above ground level.
This surveying instrument works by using a prism to bend the optical path at a right angle. It is set up so that the altitude and azimuth scales read 0°. When a pilot balloon is released, the theodolite tracks its position every minute. The elapsed time and the balloon’s predetermined rate of ascent, together with azimuth and angular altitude, are used to determine wind direction and speed.
Apart from pilot balloons, meteorological theodolites can also measure the angles of elevation and azimuth of other moving objects, including aircrafts and ships. With good visibility, some devices can capture such measurements even from a distance of 20,000 meters or more.
Choosing the Right Meteorological Theodolite
With the aid of a pilot balloon theodolite, meteorologists can determine angles of elevation and azimuth or the direction of a celestial object from a particular observer. As stated, it’s also designed to determine wind direction and wind speed given a specific altitude.
When choosing meteorological theodolites, you have to select a device that can measure objects at great distances. Such instruments are more useful and reliable in predicting atmospheric phenomena.
You should also look at several helpful features. For instance, theodolites with an internal illumination system can be advantageous if you’re operating in low-light conditions. Having an automatic power-down feature will also help eliminate unnecessary power drain.
If a theodolite’s mechanical system can independently operate from its electronic system, it will further allow you to use your tool even when there’s power loss.
Apart from providing top-quality theodolites, your supplier should also provide repair services to help you maintain your tools cost-effectively and, subsequently, let you perform your job more efficiently.
Electronic Meteorological Theodolites for Surveyors and Weather










Comments